Use this link for review flash cards
Fundamentals of WANs and IP Routing: Connecting the World
Wide Area Networks (WANs) and IP routing are the backbone of global connectivity, allowing data to traverse vast distances and connect networks across the world. In this article, we'll delve into the basics of WANs, the role of IP routing, and how these technologies enable the seamless exchange of information on a global scale.
What is a WAN?
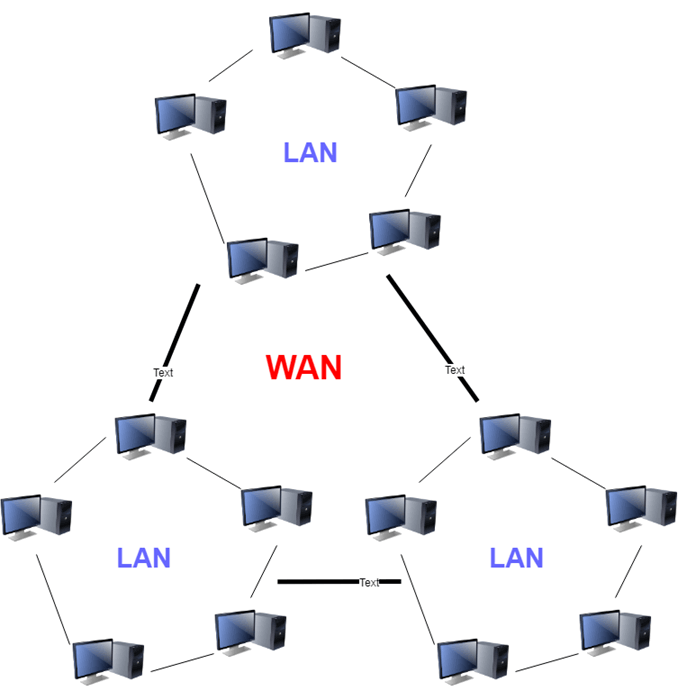
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that spans a large geographic area, connecting multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) and individual devices over long distances. Unlike LANs, which typically cover a single location like an office or home, WANs can span cities, countries, or even continents. The internet itself is the most prominent example of a global WAN.
Key Components of WANs
1. Routers
Routers are the central devices in WANs responsible for forwarding data packets between different networks. They make decisions based on destination IP addresses, determining the most efficient path for data to reach its destination.
2. Links and Transmission Lines
WANs use various transmission media, including fiber optics, satellite links, and undersea cables, to connect geographically distant locations. These links ensure data can travel across long distances.
3. Protocols
WANs rely on specific protocols for communication, including the Internet Protocol (IP) suite. IP addresses are used to identify devices and networks on a WAN, while protocols like BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) help routers exchange routing information.
4. Cloud Services
In recent years, cloud services have become a crucial part of WANs, offering scalable and cost-effective solutions for data storage, processing, and delivery.
IP Routing in WANs
IP routing is the process by which data packets are directed from their source to their destination across interconnected networks. It's a fundamental concept in WANs and plays a pivotal role in enabling global connectivity. Here's how it works:
Source to Destination: When data is sent from one device to another, the sender's router determines the best path to the destination based on the destination IP address.
Routing Tables: Routers maintain routing tables that contain information about known networks and the best routes to reach them. These tables are continually updated to adapt to changing network conditions.
Packet Forwarding: Routers forward data packets from one router to the next, following the path outlined in the routing tables.
Interconnected Networks: Data packets may pass through multiple routers and networks on their journey, crossing WAN boundaries and traversing vast distances.
Destination Arrival: The data packet finally reaches its destination network, where the recipient's router ensures delivery to the correct device.
Conclusion
WANs and IP routing are the technological pillars that enable global communication and connectivity. From the internet to private corporate networks, these technologies make it possible for data to flow seamlessly across vast distances.
As you delve deeper into the world of networking and explore your interests in technology, understanding the fundamentals of WANs and IP routing will open doors to exciting opportunities in the field. The ability to connect networks and facilitate data transfer across the globe is a powerful skill that continues to shape our digital world.
In future articles, we'll explore advanced topics in WAN design, routing protocols, and emerging technologies that are transforming the way we connect and communicate on a global scale. Stay curious and keep building your knowledge!